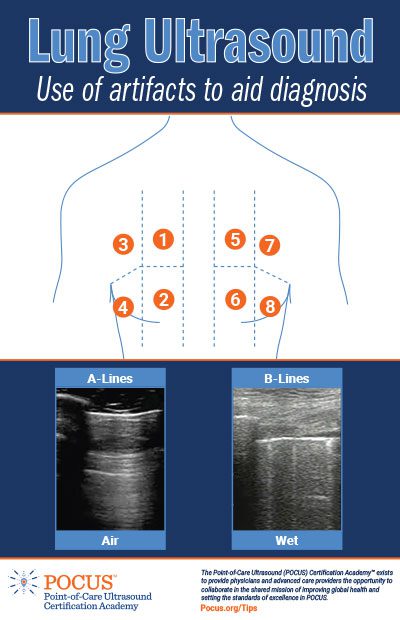
This infographic explores artifacts in point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) to aid diagnosis when performing a ultrasound on the lungs. Note the differences between the A-lines and B-lines scans.
A Lines
Multiple repeating horizontal lines that are parallel and equidistant from the pleura.
This can be a normal finding in the healthy patient (dry lung) but, A lines may also be prominent in patients with atelectasis, asthma, COPD (positive lung sliding at pleural line), and pneumothorax (negative lung sliding at pleural line).
B Lines
Transient, hyperechoic vertical lines that extend from the pleura to the bottom of the screen at a depth of 16cm.
Less than 2 B lines in any given region can be a normal finding; 3 or more B lines in any given region is pathologic (Wet Lung).
Focal B lines may suggest pneumonia, whereas diffuse B lines in 3 or more zones on both sides of the chest suggests a diffuse alveolar interstitial syndrome such as pulmonary edema or ARDS. With focal or diffuse B lines with spared regions of the pleura that lack B lines, a focal or bilateral pneumonia may be present or there could be signs of pulmonary embolism (focal, hypoechoic subpleural region) or cancer (focal or diffuse; hyperechoic)