It is no secret that technology has and will continue to transform our lives. It’s anyone’s guess to the extent of change it will create in shaping and molding our future. There isn’t a sector that technology does not have a hand in. It is all around us and will impact every and anything, including the world of medicine.

Telemedicine
One incredible way we bear witness to this taking flight is in telemedicine, medicine utilizing technology to deliver care at a distance. Gone are the days of having to be in the same room with a patient to render care. Remote technology has removed location out of the care equation. Via HIPAA compliant video-conferencing tools, modern technology has enabled doctors to consult patients without the need to be physically present with each other. In its simplest terms, telemedicine is the remote delivery of healthcare services.
Healthcare providers use telemedicine for the transmission of digital imaging, video consultations, and remote medical diagnosis. There are three common types of telemedicine performed.
- Interactive Medicine – patients and physicians communicate in real-time, utilizing HIPAA compliant tools.
- Store and Forward – providers are permitted to share patient information with a practitioner in a different location.
- Remote Patient Monitoring or Diagnosis – allows remote monitoring or diagnosis of patients located in another facility or residing at home using mobile medical devices to collect data.
Distance No Longer A Barrier
According to the World Health Organization, telemedicine is “healing from a distance.” Patients are no longer held captive by their location in defining the level of healthcare they have access to. Secure video, audio connections, and artificial intelligence allow specialists to treat patients who reside in regions with limited access to care. A physician in one area uses a telecommunications infrastructure to deliver care to patients regardless of where they live.
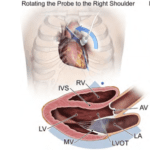
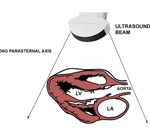
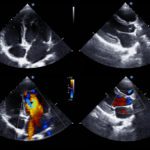
The depth of this developed technology has provided modality advancements used to learn about a patient’s condition. As telemedicine evolves and shortens the distance gap between provider and patient, the impact is felt throughout the medical community to include ultrasonography. As ultrasound machines grow in portability and as technologies to support data transmission become readily available, adequate infrastructure has made way for the emergence of tele-ultrasound.
Tele-ultrasound
Tele-ultrasound involves performing bedside ultrasound from one location with images transmitted and interpreted by a provider located in an entirely separate geographic area. There are two methods for applying this process, synchronous or asynchronous. Asynchronous tele-ultrasound employs a store-and-forward technique. Images are captured, stored, and later transmitted for image interpretation. Synchronous tele-ultrasound, however, is conducted in real-time.
The most common use of this is when there is no healthcare expert available, but the situation calls for a specialist. The patient is still able to benefit from medical expertise via remote interpretation. The healthcare provider located with the patient performs the examination and is assisted by a medical expert, not attending the examination site.
Although the specialist is remote, he/she manipulates the ultrasound probe on the patient utilizing a robotic arm. The expert site and the patient site are connected by a secure internet connection via a telemedicine platform to ensure a safe, concurring exchange of information.
Benefits
The popularity of tele-ultrasound is increasing as it has contributed significantly to global healthcare. Patient care is exceedingly limited by a lack of access to trained clinicians, even in high-income countries. Considerably so in resource-limited settings, where a supply and demand mismatch is even further exaggerated. Low-income regions suffer from economic constraints that prohibit even the best practitioners from providing the required level of care. Deploying tele-ultrasound in such communities is rapidly growing to contribute to closing the quality healthcare gap distance creates.
Patients residing in rural areas who once had difficulties accessing medical attention now have virtual reach. Telemedicine and tele-ultrasound have made healthcare more accessible and cost-effective, increasing patient engagement.
- Information is shared between physicians and patients instantaneously
- Providers can see and capture readings from medical devices at a separate location
- Doctor visits for diagnosis and treatment can occur without waiting for an appointment or leaving home
These benefits are only the tip of the iceberg. It is clear with just those noted here, tele-ultrasound is here to eliminate distance barriers and improve access to medical services that would otherwise not be available in rural communities. It facilitates collaboration outside of time and space—crossing all borders to include international ones, fostering a future for international collaboration. Soon, medical support and advances available to one country but not another won’t limit access.
Technological advancement, like telemedicine and tele-ultrasound, is changing the entire healthcare infrastructure. The future will only continue to enhance sharing capabilities and enlarging our reach, permitting patients to receive the best care possible, no matter where they are.
Ready to get started on your POCUS journey? Check out our many certificates and certifications here.
Looking for additional inspiration? Sign up for our POCUS Post™ newsletter to receive monthly tips and ideas.