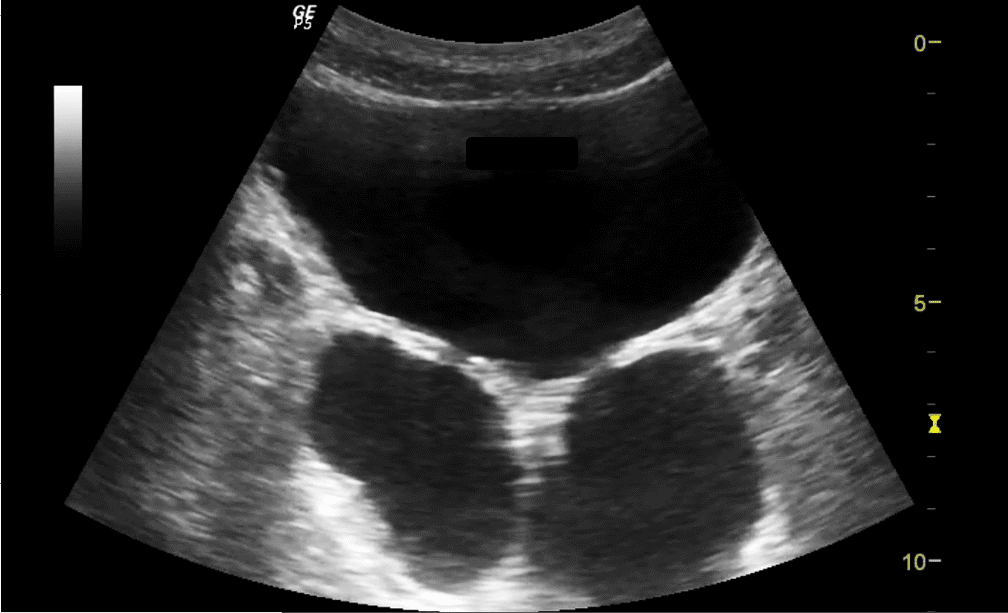
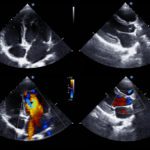
A 65-year-old male patient presents to the emergency department with a history of recurrent UTI and lower abdomen discomfort. The ultrasound fellow decides to perform a POCUS bladder scan to rule out bladder pathology. The following image was obtained in the transverse plane.
What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Free fluid in the pelvic cavity
B. Cysts
C. Bladder diverticulum/diverticula
D. Bladder stones
The most likely answer is bladder diverticulum/diverticula.
Explanation
A bladder diverticulum is an out-pouching of the bladder mucosa through a defect in the muscular wall. It may be congenital or acquired, often secondary to conditions causing bladder outlet obstruction such as benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH), and neurogenic bladder. Ultrasound is an excellent, non-invasive first-line imaging modality for the detection of bladder diverticula.
On ultrasound, a bladder diverticulum typically appears as a round or oval anechoic structure adjacent to the bladder and connected to the bladder lumen by a narrow neck. Patients may present with recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs), urinary retention, or lower urinary tract symptoms. Bladder diverticula could also be an incidental finding in some patients. Sometimes, calculus could be present in the diverticula as well.
References